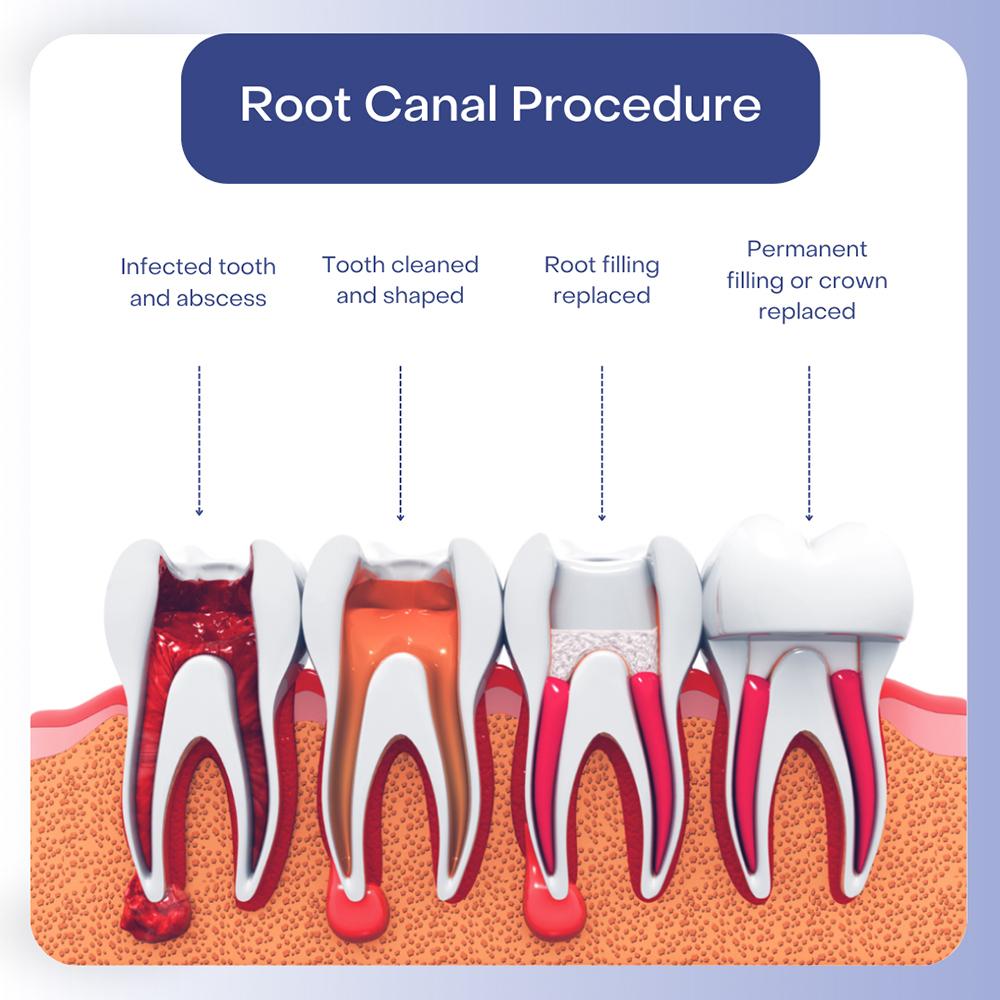
Root canals can indeed have systemic effects on the body due to several factors related to chronic infection, inflammation, and immune system dysregulation. Here’s a breakdown of how infected root canals can lead to health issues such as brain fog, autoimmune diseases, and even neurological conditions like Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis (MS), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), as well as the mechanisms of action involved.
Mechanisms of Root Canal-Related Health Problems
1. Chronic Low-Grade Infection
When a tooth undergoes a root canal, it is essentially “dead” tissue that is no longer supplied by blood vessels or nerves. This creates a perfect environment for bacteria to thrive in the remaining microscopic tubules within the tooth. Complete sterilization of these spaces is nearly impossible, and bacteria can persist. These bacteria release toxins and inflammatory by-products, which can leak into surrounding tissues and enter the bloodstream, leading to chronic inflammation throughout the body.
2. Immune Dysregulation:
The immune system becomes chronically activated in response to the persistent infection in the root canal. As bacteria continue to release endotoxins and exotoxins, the immune system struggles to eliminate them. This can lead to immune dysregulation, where the immune system begins to overreact to benign stimuli, triggering autoimmune diseases. Some of these diseases include conditions like multiple sclerosis (MS) and ALS, as chronic inflammation and immune activation have been linked to neurodegenerative conditions.
3. Biofilm Formation:
Root canals are particularly prone to biofilm formation, where bacteria aggregate in protective communities that are resistant to both antibiotics and the body’s immune defenses. These biofilms can act as a persistent source of low-grade infection, continuously stimulating the immune system without being completely eradicate.
4. Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS):
In some cases, the chronic immune stimulation from an infected root canal can trigger Mast Cell Activation Syndrome (MCAS). This condition occurs when mast cells, which are part of the immune system, become dysregulated and release excessive amounts of inflammatory mediators such as histamine. This can cause symptoms ranging from brain fog and digestive issues to cardiovascular symptoms. In cases where MCAS is triggered by root canal infections, the persistent presence of bacterial toxins leads to a state of heightened immune activation.
5. Cytokine Storms and Inflammation:
Bacteria from infected root canals can trigger the release of cytokines, proteins involved in signaling during immune responses. Excessive cytokine release, known as a “cytokine storm,” can lead to widespread inflammation, tissue damage, and systemic effects that may exacerbate neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
6. Oral-Systemic Link:
The link between oral health and systemic diseases is well-established. Bacteria from an infected root canal can enter the bloodstream and travel to distant parts of the body, leading to issues such as cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and chronic inflammation. This connection between the mouth and the rest of the body highlights how untreated oral infections can have far-reaching effects on overall health.
7. Neurological Conditions:
Chronic infections, like those from root canals, may also play a role in neurodegenerative conditions. Persistent infection and inflammation can disrupt neural processes and may contribute to the development or progression of conditions like Parkinson’s disease and ALS. While more research is needed to establish direct causality, chronic inflammation and immune system dysregulation are common features of these diseases, and long-standing infections such as those in root canals may act as contributors.
Limitations of Traditional Diagnostics
One of the challenges in addressing root canal-related infections is the difficulty in diagnosing them. Standard dental X-rays are often insufficient because they only provide a two-dimensional image, which can miss infections hidden in the complex structure of the tooth. A 3D Cone Beam CT scan is far more effective at detecting these hidden infections, along with bone loss, abscesses, and other dental pathologies that can contribute to systemic health issues.
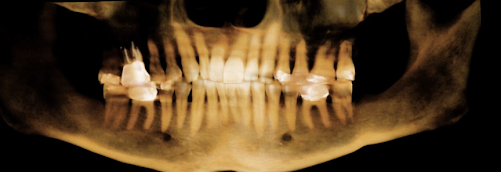
Evidence from the Literature
• Systemic effects of oral infections: Research has shown that oral infections, including those originating from root canals, can contribute to systemic inflammation and disease. Studies link chronic oral infections to cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
• Biofilm resistance: Research on biofilms highlights their role in persistent infections. Biofilms in root canals are particularly resistant to standard treatments, making it difficult to fully clear the infection. This ongoing presence of bacteria may be a driving force behind the systemic effects seen in patients with root canal infections.
In summary, the infection left behind in root canals can serve as a reservoir of bacteria that leads to chronic inflammation, immune dysregulation, and potential systemic effects, including neurological and autoimmune diseases. The use of advanced diagnostics like 3D Cone Beam CT scans can help in identifying these issues, which are often missed by standard X-rays.
For those looking for further insights, in our podcast below, we discuss how chronic inflammation triggered by infected root canals could potentially exacerbate conditions like MCAS. Watch it to learn more: