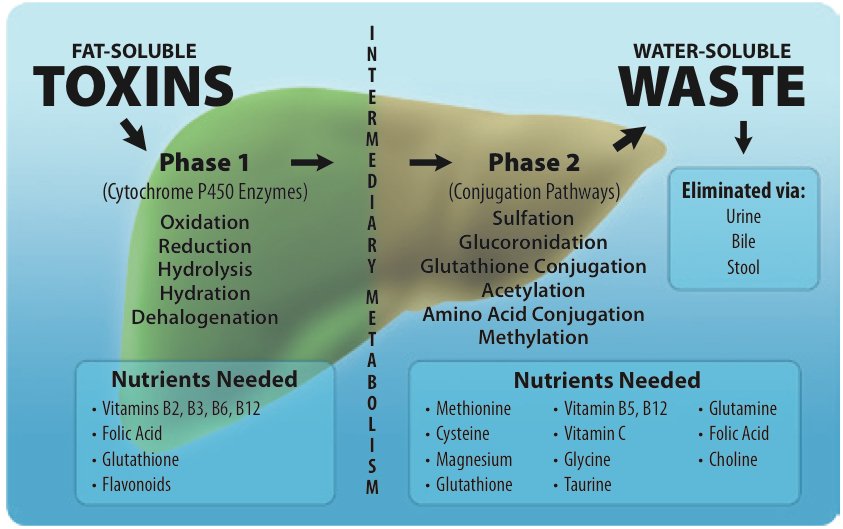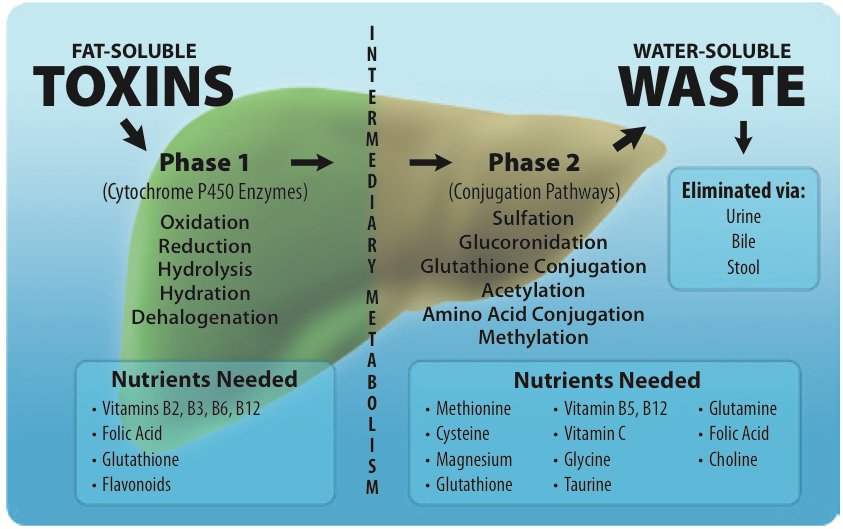
Glucuronidation is a crucial Phase II process that helps convert toxins, drugs, and carcinogens into less harmful forms. It plays a significant role in transforming foreign substances (xenobiotics) into water-soluble compounds that the body can easily excrete through urine or bile. This detoxification system utilizes a substance called glucuronic acid, also known as Glucarate, to attach to and deactivate various drugs and components from our diet.
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the Glucuronidation process:
-
Glucarate coats cells.
-
Harmful substances attack cells.
-
Glucuronidation removes these harmful substances from cells, making them water-soluble and allowing the body to eliminate them.
-
Occasionally, a harmful enzyme can reverse glucuronidation, releasing toxins back into the body.
-
Glucarate from the cell binds to the enzyme, preventing its harmful actions.
You can find Glucarate or Glucuronic Acid in small amounts in foods like broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, apples, grapefruit, and oranges. Due to the increasing toxin exposure in our environment, our bodies may struggle to keep up with detoxification demands. Supplementing with an advanced form of Glucarate, such as D-Glucaric acid (Calcium D-Glucurate), has been shown to support the body’s natural detoxification system (Glucuronidation). This can enhance the elimination of toxins like Bis-Phenol A, Phthalates, Heavy Metals, Mold, Glyphosate, and other harmful substances. Combining it with muramyl peptide and beta-glucan can further improve the detoxification process. This reduction in toxicity levels can typically be observed within about three months. It’s advisable to conduct a toxicity panel before and after this therapy to establish a baseline.
If you want more information on how to support your Glucuronidation pathway or assess environmental toxicity, please reach out to our office. We’re here to help.